1 虚函数和纯虚函数的作用
定义一个函数为虚函数,不代表函数为不被实现的函数。
定义他为虚函数是为了允许用基类的指针来调用子类的这个函数。
定义一个函数为纯虚函数,才代表函数没有被实现。
定义纯虚函数是为了实现一个接口,起到一个规范的作用,规范继承这个类的程序员必须实现这个函数。
https://blog.csdn.net/Hackbuteer1/article/details/7558868
c++中的虚函数是为了实现多态而诞生的,纯虚函数是为了实现抽象类的概念,这两个函数的作用都是为了增强c++语言的面向对象编程能力。话不多说,直接上代码案例。
2 虚函数
虚函数为了实现多态,也就是同一个函数有多种不同的形态。在程序应用中,可以这么理解,就是用父类的指针去调用子类中的方法,这样就大大较少了程序中的代码量,可以用一个指针调用其所有派生类中的方法,使得编程的代码量又大大减少。
2.1 虚函数的定义
虚函数的定义很简单,就是在该函数前面加一个virtual关键字,告诉编译器,这是一个虚函数。形式如下:
父类中的写法:
1
| virtual void say(){cout << " this is saying... " << endl;}
|
子类中的写法:
子类中可以带有virtual关键字,也可以不带。
1
2
3
4
|
virtual void say(){cout << " this is saying... " << endl;}
void say(){cout << " this is saying... " << endl;}
|
2.2 代码案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| #include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
int a;
public:
Base(int m) :a(m) {}
Base() {}
void funcA() { cout << "in void Base::funcA" << endl; }
virtual void funcB() { cout << "in virtual void Base::funcB" << endl; }
};
class child :public Base {
public:
int b;
public:
child(int m, int n) :Base(m), b(n) {}
child() {}
void funcA() { cout << "in void child::funcA" << endl; }
virtual void funcB() { cout << "in virtual void child::funcB" << endl; }
void funcC() { cout << "in child func C"<<endl; }
};
int main() {
Base* c = new child;
child* cc = new child;
c->funcA();
c->funcB();
cc->funcA();
cc->funcB();
return 0;
}
|
从代码中看,指针c其实是父类Base的指针,但是对于声明了虚函数的方法,却可以调用其派生类中的方法,没有声明虚函数,则只能调用父类的方法。因为指针c是父类类型的指针。结果如下:

3 纯虚函数
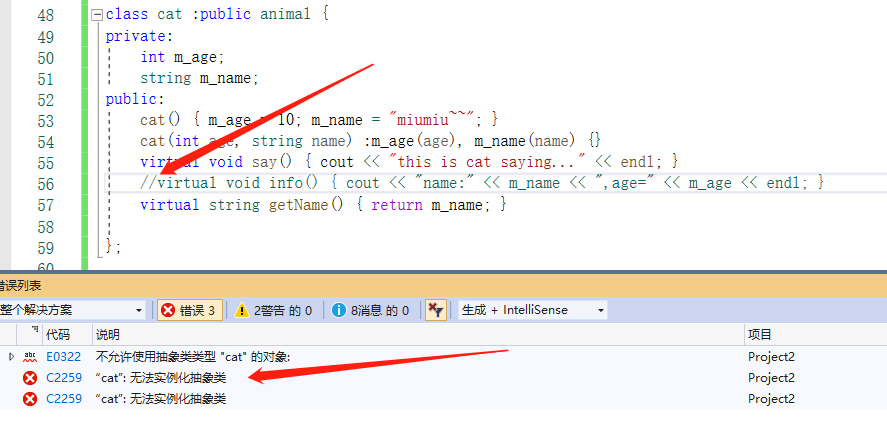
纯虚函数的作用是为了实现抽象类,也就是定义接口规范,这样就为编程省下了很多的沟通成本,因为程序员不能违反这个规范进行自定义接口,所有的接口都由抽象类定义好之后才由程序员去实现其具体的功能。该抽象类不能被实例化,只有其派生类实现了抽象类中的**所有的**纯虚函数才能被实例化,如果其中有一个纯虚函数没有被重写,那么该派生类还是不能被实例化,如下图所示:
3.1 纯虚函数的定义
纯虚函数的定义和虚函数的定义类似,不同之处就是该类不需要被实现,且需要以=0结尾,以告诉编译器,这是一个纯虚函数。如下:
父类写法:
子类写法:
虚函数在子类中可以带virtual关键字,也可以不带。
1
2
3
4
|
virtual void say(){cout <<"say"<<endl;}
void say(){cout <<"say"<<endl;}
|
3.2 代码案例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| class animal {
public:
virtual void say()= 0;
virtual void info() = 0;
virtual string getName() = 0;
};
class dog :public animal {
private:
int m_age;
string m_name;
public:
dog() { m_age = 0; m_name = "wangwang"; }
dog(int age, string name) :m_age(age), m_name(name) {}
void say() { cout << "this is dog saying..." << endl; }
void info() { cout << "name:" << m_name << ",age=" << m_age << endl; }
string getName() { return m_name; }
};
class cat :public animal {
private:
int m_age;
string m_name;
public:
cat() { m_age = 10; m_name = "miumiu~~"; }
cat(int age, string name) :m_age(age), m_name(name) {}
void say() { cout << "this is cat saying..." << endl; }
void info() { cout << "name:" << m_name << ",age=" << m_age << endl; }
string getName() { return m_name; }
};
int main() {
animal *d = new dog(100,"我是狗");
d->info();
d->say();
cout << d->getName() << endl;
cout << "----" << endl;
d = new cat(120,"我是猫");
d->say();
d->info();
cout << d->getName() << endl;
return 0;
}
|
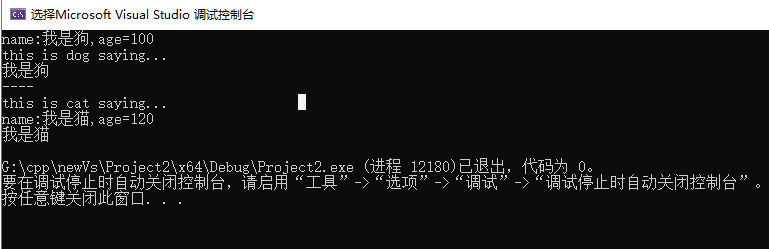
从代码中可以看到,虚函数,animal类定义了一个规范,就是动物类的规范,所有该类的派生类都必须实现其中的所有的纯虚函数,才能被实例化。运行结果如下:
写在最后
欢迎大家关注鄙人的公众号【麦田里的守望者zhg】,让我们一起成长,谢谢。