1 二叉树的定义
在计算机科学 中,二叉树 (英语:Binary tree)是每个节点最多只有两个分支(即不存在分支度大于2的节点)的树结构 。通常分支被称作“左子树”或“右子树”。二叉树的分支具有左右次序,不能随意颠倒。
二叉树的第$i$层至多拥有$2^{i-1}$个节点;深度为$k$的二叉树至多总共有$2^k-1$个节点(定义根节点所在深度$k_0=0$),而总计拥有节点数符合的,称为“满二叉树”;深度为$k$有$n$个节点的二叉树,当且仅当其中的每一节点,都可以和同样深度的满二叉树,序号为1到$n$的节点一对一对应时,称为完全二叉树 。对任何一棵非空的二叉树$T$,如果其叶片(终端节点)数为$n_0$,分支度为2的节点数为$n_2$,则$n_0=n_2+1$。
与普通树不同,普通树的节点个数至少为1,而二叉树的节点个数可以为0;普通树节点的最大分支度没有限制,而二叉树节点的最大分支度为2;普通树的节点无左、右次序之分,而二叉树的节点有左、右次序之分。
二叉树通常作为数据结构应用,典型用法是对节点定义一个标记函数,将一些值与每个节点相关系。这样标记的二叉树就可以实现二叉搜索树 和二叉堆 ,并应用于高效率的搜索和排序。
2 完全二叉树和满二叉树
完全二叉树 满二叉树
总节点k
$2^{h-1}<=k<=2^h-1$
$k=2^h-1$
树高h
$h=log_2k+1$
$h=log_2{(k+1)}$
3 二叉树的遍历 3.1 先序遍历 先序遍历的顺序是:先根节点,再左节点,再右节点,即根节点->左节点->右节点。
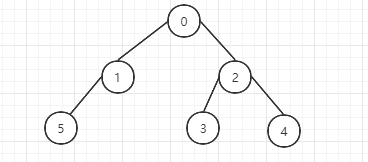
如:
先序遍历的顺序为:0,1,5,2,3,4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void beforeOrder (MyTreeNode root) { if (root != null ) { System.out.println(root.data); beforeOrder(root.leftChild); beforeOrder(root.rightChild); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public void preOrder (MyTreeNode root) { QueueToStack<MyTreeNode> stack = new QueueToStack <>(); stack.push(root); MyTreeNode node; while (!stack.empty()){ node = stack.pop(); System.out.println(node.data); if (node.rightChild!=null ){ stack.push(node.rightChild); } if (node.leftChild!=null ){ stack.push(node.leftChild); } } }
3.2 中序遍历 中序遍历的顺序为,先左节点,再根节点,再右节点,即左节点->根节点->右节点。
还是以下面的二叉树为例:
中序遍历的顺序为:5,1,0,3,2,4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void middleOrder (MyTreeNode root) { if (root != null ) { middleOrder(root.leftChild); System.out.println(root.data); middleOrder(root.rightChild); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public void inOrder (MyTreeNode root) { QueueToStack<MyTreeNode> stack = new QueueToStack <>(); MyTreeNode node = root; while (node != null || !stack.empty()) { while (node != null ) { stack.push(node); node = node.leftChild; } if (!stack.empty()) { node = stack.pop(); System.out.println(node.data); node = node.rightChild; } } }
3.3 后序遍历 后序遍历的顺序是:先左节点,再右节点,再根节点,即左节点->右节点->根节点。
还是以上面的二叉树为例:
后序遍历的顺序为:5,1,3,4,2,0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void behindOrder (MyTreeNode root) { if (root != null ) { behindOrder(root.leftChild); behindOrder(root.rightChild); System.out.println(root.data); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public void afterOrder (MyTreeNode root) { QueueToStack<MyTreeNode> stack = new QueueToStack <>(); MyTreeNode node = root; MyTreeNode lastVisit = root; while (!stack.empty() || node != null ) { while (node != null ) { stack.push(node); node = node.leftChild; } node = stack.top(); if (node.rightChild==null ||node.rightChild==lastVisit){ System.out.println(node.data); stack.pop(); lastVisit = node; node=null ; }else { node = node.rightChild; } } }
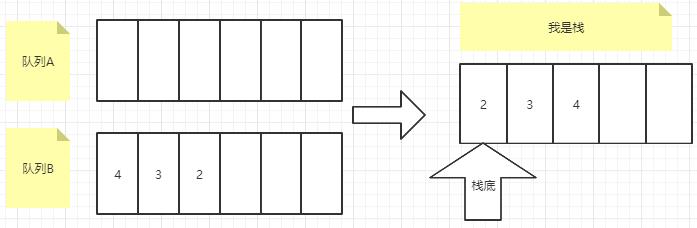
非递归实现2
我们知道,二叉树的前中后的遍历依次为以下顺序:
前序遍历:root->left->right。
中序遍历:left->root->right
后序遍历:left->right->root
我们发现后序遍历和前序遍历有些地方比较相似,我们可以借鉴前序遍历的非递归实现,从而快速实现后续遍历的非递归实现。我们发现后续遍历相当于 是前序遍历的一个反序,只不过反过来之后将左右孩子的遍历顺序交换了一下,但是没有关系,我们先来回顾一下前序遍历的非递归实现代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return res; Deque<TreeNode> stk = new ArrayDeque <>(); stk.addLast(root); while (!stk.isEmpty()) { TreeNode t = stk.pollLast(); res.add(t.val); if (t.right != null ) stk.addLast(t.right); if (t.left != null ) stk.addLast(t.left); } return res; }
从代码中可以看待,因为栈是一种先进后出 的数据结构,所以如果前序遍历想要先访问左子树,那么就需要先将右子树压入栈中。同理,在后序遍历中,我们将后序遍历的顺序反序遍历,将left->right->root的遍历顺序改成root->right->left。那么在添加到结果集的时候,也需要对其添加顺序进行反序,所以就有了下面的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return res; Deque<TreeNode> stk = new ArrayDeque <>(); stk.addLast(root); while (!stk.isEmpty()) { TreeNode t = stk.pollLast(); res.add(0 , t.val); if (t.left != null ) stk.addLast(t.left); if (t.right != null ) stk.addLast(t.right); } return res; }
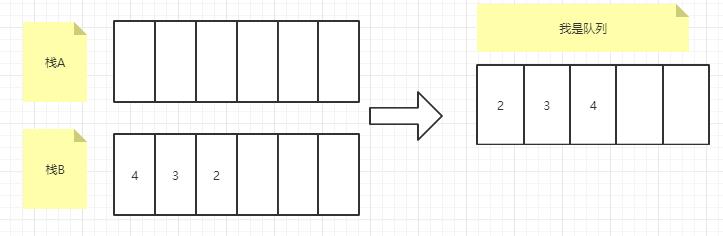
3.4 广度优先遍历 广度优先遍历的顺序是:从根节点向下,从左到右遍历,下面还是拿上面的二叉树为例:
广度优先遍历顺序为:0,1,2,5,3,4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public void breadthOrder (MyTreeNode root) throws InterruptedException { StackToQueue<MyTreeNode> queue = new StackToQueue (); queue.push(root); while (queue.size() > 0 ) { root = queue.pop(); System.out.println(root.data); if (root.leftChild != null ) queue.push(root.leftChild); if (root.rightChild != null ) queue.push(root.rightChild); } }
3.5 深度优先遍历 深度优先遍历的顺序为:先从根节点一直往下直到叶子节点进行遍历,然后叶子节点回到其父节点的右节点进行遍历。
深度优先遍历顺序:0,1,5,2,3,4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void deepthOrder(MyTreeNode root) { QueueToStack<MyTreeNode> stack = new QueueToStack(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.empty()) { root = stack.pop(); System.out.println(root.data); if (root.rightChild != null) stack.push(root.rightChild); if (root.leftChild != null) stack.push(root.leftChild); } }
4 二叉树的实现 4.1 QueueToStack.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 package tree;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.Queue;public class QueueToStack <T> { Queue<T> queueA = new LinkedList <>(); Queue<T> queueB = new LinkedList <>(); public void push (T x) { if (queueA.isEmpty() && !queueB.isEmpty()) { queueA.add(x); while (!queueB.isEmpty()){ T data = queueB.remove(); queueA.add(data); } } else if (!queueA.isEmpty() && queueB.isEmpty()) { queueB.add(x); while (!queueA.isEmpty()){ T data = queueA.remove(); queueB.add(data); } } else if (queueA.isEmpty() && queueB.isEmpty()) { queueA.add(x); } } public T pop () { if (queueA.isEmpty() && !queueB.isEmpty()) return queueB.remove(); return queueA.remove(); } public T top () { if (queueA.isEmpty() && !queueB.isEmpty()) return queueB.peek(); return queueA.peek(); } public boolean empty () { if (queueA.isEmpty() && queueB.isEmpty()) return true ; return false ; } }
4.2 StackToQueue.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 package tree;import java.util.Stack;public class StackToQueue <T> { Stack<T> stackA = new Stack <>(); Stack<T> stackB = new Stack <>(); public void push2 (T data) { if (stackA.empty() && !stackB.empty()) { while (!stackB.empty()) { stackA.push(stackB.pop()); } } stackA.push(data); } public T pop2 () { if (stackA.empty() && stackB.empty()) return null ; else if (!stackA.empty()) { while (!stackA.empty()) stackB.push(stackA.pop()); return stackB.pop(); } else return stackB.pop(); } public T peek2 () { if (stackA.empty() && stackB.empty()) return null ; else if (!stackA.empty()) { while (!stackA.empty()) stackB.push(stackA.pop()); return stackB.peek(); } else return stackB.peek(); } public void push (T x) { if (stackA.empty()) { stackA.push(x); } else { while (!stackA.empty()) stackB.push(stackA.pop()); stackA.push(x); while (!stackB.empty()) stackA.push(stackB.pop()); } } public T pop () { if (!stackA.empty()) return stackA.pop(); return null ; } public void peek () { if (!stackA.empty()) System.out.println(stackA.peek()); } public int size () { return stackA.size(); } }
4.3 MyTreeNode.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 package tree;public class MyTreeNode <T> { T data; MyTreeNode leftChild; MyTreeNode rightChild; public void addLeftChild (T data) { if (data != null ) this .leftChild = new MyTreeNode (data); } public void addRightChild (T data) { if (data != null ) this .rightChild = new MyTreeNode (data); } public MyTreeNode (T data) { this .data = data; } public MyTreeNode () { this .data = null ; this .leftChild = null ; this .rightChild = null ; } public MyTreeNode (T data, MyTreeNode leftChild, MyTreeNode rightChild) { this .data = data; this .leftChild = leftChild; this .rightChild = rightChild; } public boolean isLeaf () { if (this .leftChild == null && this .rightChild == null ) { return true ; } return false ; } public void beforeOrder (MyTreeNode root) { if (root != null ) { System.out.println(root.data); beforeOrder(root.leftChild); beforeOrder(root.rightChild); } } public void preOrder (MyTreeNode root) { QueueToStack<MyTreeNode> stack = new QueueToStack <>(); stack.push(root); MyTreeNode node; while (!stack.empty()) { node = stack.pop(); System.out.println(node.data); while (node.rightChild != null ) { stack.push(node.rightChild); } while (node.leftChild != null ) { stack.push(node.leftChild); } } } public void middleOrder (MyTreeNode root) { if (root != null ) { middleOrder(root.leftChild); System.out.println(root.data); middleOrder(root.rightChild); } } public void inOrder (MyTreeNode root) { QueueToStack<MyTreeNode> stack = new QueueToStack <>(); MyTreeNode node = root; while (node != null || !stack.empty()) { while (node != null ) { stack.push(node); node = node.leftChild; } if (!stack.empty()) { node = stack.pop(); System.out.println(node.data); node = node.rightChild; } } } public void behindOrder (MyTreeNode root) { if (root != null ) { behindOrder(root.leftChild); behindOrder(root.rightChild); System.out.println(root.data); } } public void afterOrder (MyTreeNode root) { QueueToStack<MyTreeNode> stack = new QueueToStack <>(); MyTreeNode node = root; MyTreeNode lastVisit = root; while (!stack.empty() || node != null ) { while (node != null ) { stack.push(node); node = node.leftChild; } node = stack.top(); if (node.rightChild==null ||node.rightChild==lastVisit){ System.out.println(node.data); stack.pop(); lastVisit = node; node=null ; }else { node = node.rightChild; } } } public void breadthOrder (MyTreeNode root) throws InterruptedException { StackToQueue<MyTreeNode> queue = new StackToQueue (); queue.push(root); while (queue.size() > 0 ) { root = queue.pop(); System.out.println(root.data); if (root.leftChild != null ) queue.push(root.leftChild); if (root.rightChild != null ) queue.push(root.rightChild); } } public void deepthOrder (MyTreeNode root) { QueueToStack<MyTreeNode> stack = new QueueToStack (); stack.push(root); while (!stack.empty()) { root = stack.pop(); System.out.println(root.data); if (root.rightChild != null ) stack.push(root.rightChild); if (root.leftChild != null ) stack.push(root.leftChild); } } }
4.4 MyBinaryTree.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 package tree;public class MyBinaryTree <T> { MyTreeNode root = null ; public MyBinaryTree (T data) { MyTreeNode<T> myTreeNode = new MyTreeNode <>(); this .root = myTreeNode; this .root.data = data; } public MyBinaryTree () { MyTreeNode<T> myTreeNode = new MyTreeNode <>(); this .root = myTreeNode; this .root.data = null ; } public void createBinaryTree (T[] dataArray, MyTreeNode root) { StackToQueue<MyTreeNode> queue = new StackToQueue (); this .root.data=dataArray[0 ]; MyTreeNode parent; queue.push(root); for (int i = 0 ; i < dataArray.length / 2 ; i++) { parent = queue.pop(); parent.addLeftChild(dataArray[2 *i+1 ]); queue.push(parent.leftChild); parent.addRightChild(dataArray[2 *i+2 ]); queue.push(parent.rightChild); } } public void beforeOrder () { root.beforeOrder(root); } public void preOrder () { root.preOrder(root); } public void middleOrder () { root.middleOrder(root); } public void inOrder () { root.inOrder(root); } public void behindOrder () { root.behindOrder(root); } public void afterOrder () { root.afterOrder(root); } public void breadthOrder () { try { root.breadthOrder(root); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public void deepthOrder () { root.deepthOrder(root); } }
写在最后 欢迎大家关注鄙人的公众号【麦田里的守望者zhg】,让我们一起成长,谢谢。